A standard halogen headlight typically uses between 55 and 60 watts. LED headlights can vary, often using between 20 and 30 watts.
Selecting the right headlight for your vehicle involves Appreciating wattage, which affects brightness and energy consumption. Traditional halogen headlights are the most common and have been the standard for decades, known for their simple design and ease of replacement. However, modern vehicles are increasingly equipped with LED headlights that offer improved efficiency and longer lifespans.
Appreciating the wattage is vital for car owners aiming for optimal performance and durability. The wattage indicates the power consumption and potential brightness, directly impacting nighttime visibility and safety. With advancements in automotive lighting technology, knowing your headlight’s wattage helps ensure you make informed maintenance and upgrade decisions for your vehicle. Let’s explain “How Many Watts Does a Standard Headlight?
Introduction To Vehicle Headlights

Vehicle headlights are essential for safe driving at night or in poor visibility conditions. These front-facing lights illuminate the path ahead, helping drivers see and be seen by others. The standard headlight wattage varies, but modern vehicles typically equip headlights ranging from 40 to 60 watts per bulb.
The Role Of Headlights In Road Safety
- Provide visibility at night or in low-light conditions.
- Allow drivers to spot obstacles, signs, and road changes early.
- Enable other road users to see the vehicle from a distance.
- Help prevent accidents by signaling the vehicle’s presence on the road.
Historical Evolution Of Vehicle Headlights
- Early 1900s: Acetylene lamps with low light output were used.
- 1930s: Introduction of the sealed beam headlamp with higher wattage.
- 1960s: Halogen headlights became popular, significantly improving brightness.
- 1990s: High-Intensity Discharge (HID) headlights offered better visibility.
- 2000s: LED headlights emerged, providing energy-efficient illumination.
Appreciating Headlight Power

Lights on your car guide the way through the dark. Your car’s headlights are vital for safety. But, have you thought about their power? In this section, we shine a light on the watts of standard headlights.
Headlights brighten roads using a certain amount of electricity. This use of electric power is measured in watts. The wattage tells you how much power the headlight needs to shine.
Factors That Affect The Power Consumption Of Headlights
- Type of Bulb: Traditional halogen bulbs differ from modern LEDs in power use.
- Headlight Design: Some models need more watts to provide the same amount of light.
- Car’s Electrical System: Older systems may not be as efficient, affecting headlight wattage.
The wattage of the headlights is not fixed. It can change based on these factors. Below is a simple table to help you understand typical headlight wattages:
| Bulb Type | Average Wattage |
|---|---|
| Halogen | 55 – 65W |
| HID | 35 – 42W |
| LED | 20 – 30W |
Smarter cars use less power for brighter light. Now, can you see how much your car’s headlights need? It’s important to know about replacements and to understand your car’s electrical load.
Types Of Headlights And Wattage Needs
Appreciating the wattage needs of various headlights is essential. It helps in selecting the right lighting for your vehicle. Different headlights use different amounts of power.
Halogen Headlights And Their Energy Consumption

Halogen headlights are the most common. They have been lighting our roads for years.
- Typical wattage: 55-65 watts per bulb
- Energy-efficiency: Compared to others, less efficient
- Brightness: Provide ample light for nighttime driving
Despite not being the most power-saving option, halogens are widely used due to their affordability.
Hid (high-intensity Discharge) Bulbs And Wattage Details
HIDs are a step up in the lighting game. They offer bright, white light.
| Type | Wattage |
|---|---|
| HID Bulbs | 35-55 watts |
They use less energy than halogens but their installation can be more complex.
Led (light Emitting Diode) Headlights And Power Efficiency
LED headlights are top-tier in efficiency. They offer longevity and superb brightness.
- Power usage: Averaging around 20-30 watts
- Life span: Excellent, often lasting as long as the vehicle
- Eco-friendly: Consume less power, reducing the car’s energy demands
LEDs provide clean, focused light beams making them a favorite for new car models.
Standard Wattage For Different Headlight Types
Choosing the right headlight bulb involves Appreciating wattage. Different headlight types have different wattage. Wattage is power. More power means more brightness. But, too much power can harm your car’s wiring.
Average Wattage Range For Halogen Headlights
Halogen headlights are common. They are not too bright or too dim. These bulbs use between 55 to 65 watts. Your car’s manual will say the exact range for your vehicle. It is important to know so you don’t overload the system.
- Low beam: typically 55 watts
- High beam: could be up to 65 watts
Standard Wattage For Hid Headlights
HID headlights, also known as Xenon lights, are brighter. They use less energy for the amount of light they produce. Most HID bulbs are 35 watts. This is lower than halogen bulbs. But, HID lights give off more light. This makes them a popular choice.
| HID Low Beam | HID High Beam |
|---|---|
| ~35 watts | ~35 watts |
Typical Wattage For LED headlights
LED headlights are the latest technology. They are very efficient. They don’t use much power. Most LED headlight bulbs range between 20 to 30 watts. This low wattage doesn’t mean they are dim. They are very bright. Their efficiency makes them a top choice for drivers.
- Standard LED: 20-30 watts
- Performance LED: may vary
Comparing Headlight Power Across Vehicle Types

Vehicle headlights are not all the same. Different vehicles need different watts for their headlights. This depends on their size and use. Let’s look at how trucks, cars, and motorcycles compare in headlight wattage.
Wattage Variations In Passenger Cars Versus Trucks
Passenger cars usually have lower-wattage headlights. They often range from 55 to 60 watts. Trucks, on the other hand, have lights that may require more power. This is because trucks are bigger and carry more weight.
Let’s check a table for a clear comparison:
| Vehicle Type | Average Headlight Wattage |
|---|---|
| Passenger Car | 55 – 60 Watts |
| Truck | 65 – 120 Watts |
Some trucks even use additional lights for better vision, which can increase total wattage.
Motorcycle Headlights: Understanding The Lower Wattage
Motorcycles have smaller engines and lighter frames. So, motorcycle headlights usually have lower wattage compared to cars and trucks.
- Typical motorcycle headlights range from 35 – 60 watts.
- Motorcycle lights need to be strong enough to light up the road.
- They must be efficient to prevent battery drain.
Motorcycles may also use LED or HID bulbs. These offer brighter light while using less power.
Impact Of Headlight Wattage On Vehicle Performance

Knowing the relationship between headlight wattage and vehicle performance is key for any car owner. Standard headlights vary in wattage but often fall within 55 to 60 watts per bulb. This might seem like a small detail, but it has a big impact on your car’s electrical system. From battery life to alternator strain, the wattage of your headlights can affect several components of vehicle performance.
How Headlight Wattage Affects Battery Life
Your car’s battery is like its heart, pumping energy to all the electrical parts. Higher-wattage headlights mean more energy is drawn from the battery. This can shorten battery life.
- A standard 55-watt headlight uses less energy than a high-wattage headlight.
- Longer-lasting headlights preserve battery health and reduce replacement needs.
Headlight Power And Its Influence On Alternator Load
The alternator, your vehicle’s generator, works harder as headlight power increases. High-wattage headlights demand more from the alternator, possibly leading to early wear.
| Headlight Wattage | Effect on Alternator |
|---|---|
| Standard (55-60W) | Moderate load |
| High Performance (Above 60W) | Heavier load |
Regulations Governing Headlight Wattage
Understanding headlight wattage is crucial for vehicle safety and road legality. Headlights illuminate the path ahead. They also signal a vehicle’s presence to others. Regulations set specific wattage limits to ensure balanced brightness. This enables clear visibility without blinding oncoming traffic.
National And International Standards For Headlight Intensity
Countries enforce standards to maintain uniform headlight intensity. The United Nations (UN) Economic Commission for Europe has established regulations, known as ECE standards. These are widely accepted in Europe and other regions. In the United States, the Department of Transportation (DOT) sets separate standards. DOT regulations often differ slightly from ECE.
- ECE standards: Up to 60/55 watts for halogen lamps.
- DOT regulations: Allow similar wattages with variations in beam patterns.
Safety Concerns And Legal Limits On Headlight Wattage
Excessive brightness leads to safety concerns such as glare. Legal limits exist to prevent this. These limits protect drivers from intense light breaches. Typical halogen headlights range between 40-60 watts. For high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps, the range is 25-28 watts. LED lamps often use less power but provide equivalent or greater light output.
Strict enforcement exists to keep headlight wattage in check. Car manufacturers must comply with these standards. Otherwise, they face penalties. Drivers can also get fines for aftermarket installation that exceeds wattage bounds.
| Type of Lamp | Typical Wattage |
|---|---|
| Halogen | 40-60W |
| HID | 25-28W |
| LED | Varies, generally lower |
Measuring And Testing Headlight Wattage
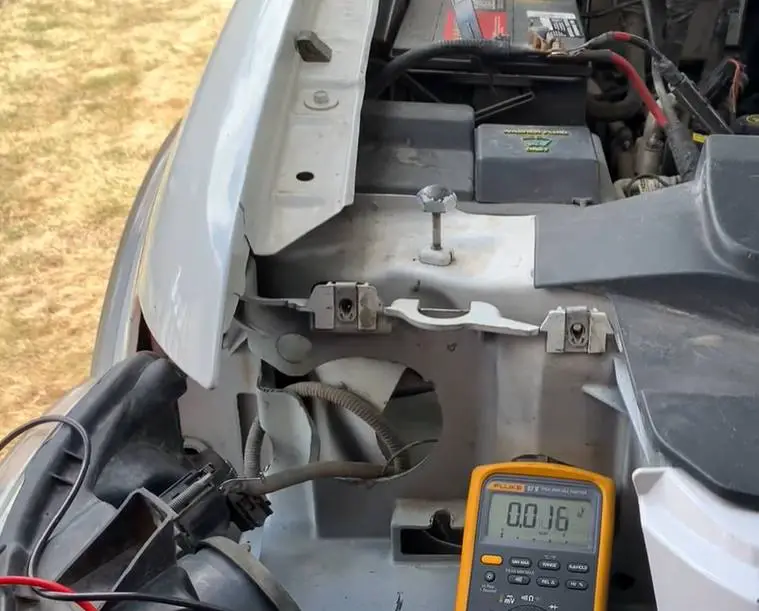

Knowing the wattage of your vehicle’s headlights is essential for road safety and compliance with regulations. Different cars have varying wattages for their headlights. The standard wattage for halogen headlights typically ranges from 55 to 65 watts. For more accurate information, measuring and testing headlight wattage is fundamental. With the right tools and methods, any car owner can perform this task.
Tools And Methods For Measuring Headlight Power
To measure your car’s headlight wattage, you’ll need specific tools:
- Multimeter: Measures voltage, current, and resistance.
- Headlight wiring diagram: Guides connections.
Follow these steps:
- Locate your car’s battery and headlight bulb on the wiring diagram.
- Set the multimeter to measure DC voltage.
- Connect the multimeter to the headlight connector’s terminals.
- Turn on the headlights to record the voltage reading.
- Use the formula Power (Watts) = Voltage x Current to calculate wattage.
Diy Approaches To Test Your Car’s Headlight Wattage
If you prefer a do-it-yourself method:
- Gather supplies: You’ll need a fully charged car battery, a multimeter, and hand gloves for safety.
- Access the headlight: Refer to the car’s manual to remove the headlight assembly safely.
- Identify wires: Find the positive and negative wires using the car’s manual.
- Measure voltage and current: Connect the multimeter and turn on the headlights to get readings.
- Calculate wattage: Apply the power formula to find the headlight’s wattage.
This DIY approach saves time and money. It also provides first-hand knowledge of your car’s electrical system.
Upgrading Your Headlights: Wattage Considerations
Thinking about upgrading your headlights? Knowing how many watts standard headlights are helps. But, wattage is just the start. Let’s dive into what you should consider before boosting your car’s visibility.
Choosing The Right Wattage For Headlight Upgrades
Match your car’s system with the right headlight wattage. Standard headlights are usually between 55 to 60 watts. Looking for more brightness? Choose higher-wattage bulbs carefully. Your car’s wiring and fuses must handle the extra power.
It’s important to check:
- Your vehicle’s manual for maximum wattage recommendations
- The type of headlight housing your car has
- Local laws, as some areas have limits on headlight wattage
Potential Drawbacks Of High-wattage Headlights
Brighter isn’t always better. High-wattage bulbs mean more heat. This can lead to damage inside the headlight or to the wiring. Other cars can suffer too. Blinding other drivers is a risk. That’s not just unsafe, it can be illegal.
Think about these points:
| Consideration | Details |
|---|---|
| Lifespan | High-wattage bulbs often burn out faster |
| Heat | More watts, more heat, potential for housing damage |
| Safety | Too bright can dazzle other drivers, increasing accident risk |
| Legality | Exceeding legal wattage can lead to fines |
Energy Efficiency And Modern Headlights

The quest for energy-efficient lighting in vehicles has revolutionized modern headlights. Current standards place emphasis not only on brightness but also on reducing power consumption. This shift impacts the number of watts traditionally used in headlights. Let’s explore the strides made in the field.
Advancements In Low-wattage, High-luminosity Headlights
Recent developments bring low-wattage bulbs to the forefront of automotive lighting. They offer high luminosity while consuming less energy. LED technology plays a major role here, drastically lowering typical wattage without compromising on performance. This is vital for electric vehicles where each watt saved extends the driving range.
| Headlight Type | Average Wattage | Luminosity (Lumens) |
|---|---|---|
| Halogen | 55-65 Watts | Approx. 1400 lm |
| LED | 20-30 Watts | Approx. 3000 lm |
| HID/Xenon | 35 Watts | Approx. 3200 lm |
Manufacturers now replace traditional halogen bulbs with LED counterparts. These use up to 60% less power.
The Future Of Headlights: Innovations That Could Change Wattage Norms
We’re witnessing a shift towards smart lighting systems. Innovations like laser headlights are pushing boundaries, offering greater efficiency. Here’s what the future holds:
- Adaptive Beam Technology – adjusts light patterns for optimum coverage and energy use.
- Laser Headlights – multiple times brighter than LEDs while being equally energy-efficient.
- Organic LEDs (OLEDs) – promise even lower wattage usage with exceptional light quality.
With these technologies, further reductions in wattage are expected while increasing safety and visibility. The automotive industry anticipates a standard that focuses on sustainability and energy efficiency.
Troubleshooting Common Headlight Wattage Issues
Hitting the road at night or during poor visibility conditions means relying heavily on your vehicle’s headlights. But what if they seem dimmer than usual or not working as expected? Knowing headlight wattage and how to fix common issues is vital for safe driving. Let’s shine some light on troubleshooting headlight wattage problems, ensuring your journey remains bright and secure.
Identifying Symptoms Of Inadequate Headlight Power
Before diving into troubleshooting, it’s important to recognize the signs of inadequate headlight power:
- Flickering lights may suggest fluctuating power or a dying bulb.
- The dimming could indicate a power supply issue or a worn-out bulb.
- Headlights that fail to turn on often point to a blown fuse or bulb.
Solving Headlight Power Issues: Tips And Tricks
Once you’ve spotted the problem, use these strategies to address headlight wattage issues:
- Check the Bulbs: Ensure they match your vehicle’s wattage requirements. Replace if necessary.
- Examine the Fuses: Look for blown fuses; these are simple and inexpensive to replace.
- Inspect the Wiring: Frayed or corroded wires can disrupt power. Consider consulting a professional.
- Adjust the Headlight Aim: Poorly aimed headlights may seem weak. Realign them for optimal performance.
- Upgrade Your Bulbs: Higher wattage or better quality bulbs can dramatically improve visibility.
Selecting The Ideal Headlight Wattage For Your Vehicle
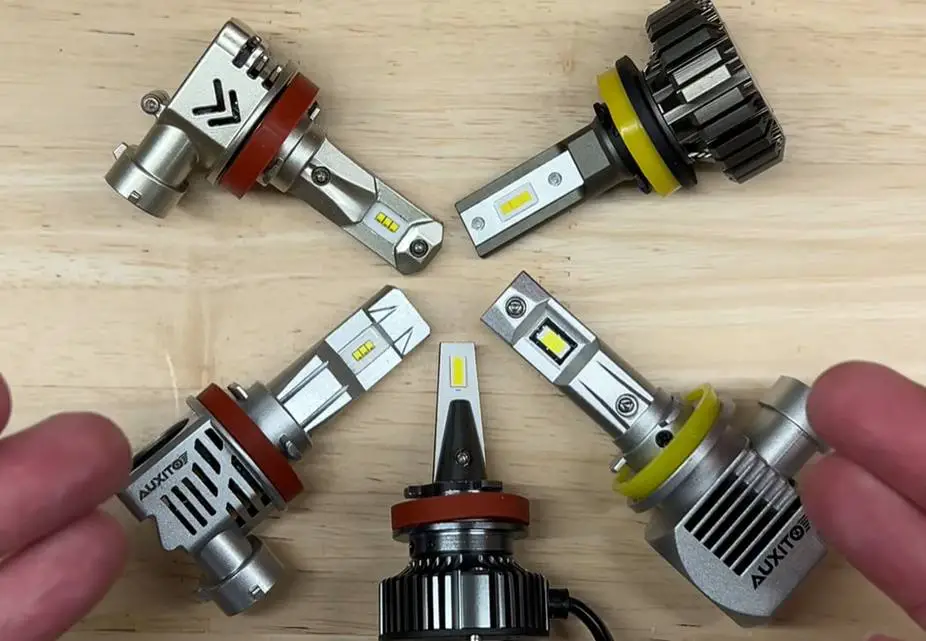

Choosing the right wattage for your vehicle’s headlights can be a game-changer for night-time driving.
It’s not only about the brightness but also about the perfect balance.
Balancing Brightness, Efficiency, And Legality
Headlight wattage determines the lamp’s brightness.
But it’s vital to consider efficiency and local laws too.
- Brighter is not always better. Overpowering headlights can cause glare.
- Efficient headlights save power and reduce strain on your vehicle’s battery.
- It’s essential to ensure the wattage is within legal limits to avoid fines.
A balance is essential. Go for the wattage that gives clear visibility without risks.
Final Thoughts On Making An Informed Headlight Wattage Choice
The ideal headlight wattage blends optimal brightness with power conservation.
Assess your needs and local regulations. Consider consulting a professional.
Make the switch to the right wattage.
It’s a smart move for safer and more efficient driving.
| Wattage | Visibility | Efficiency | Legality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 55-60W | Good | High | Usually Legal |
| 70-100W | Better | Lower | Check Local Laws |
Select the wattage that ensures your journeys are safe and your car is compliant.
Frequently Asked Questions On How Many Watts Is A Standard Headlight
How Many Watts Is A Normal Headlight?
A normal halogen headlight typically uses about 55 watts of power. Standard LED headlights often range from 20 to 30 watts.
Can I Use a 100w Headlight Bulb Instead Of 55w?
No, using a 100w headlight bulb instead of 55w risks overheating, and potential damage, and could be illegal. Always match bulb wattage with your vehicle’s specifications.
How Bright Are Normal Headlights?
Normal car headlights typically emit between 700 and 1,200 lumens of brightness. High-intensity discharge (HID) headlights can range from 3,000 to 3,500 lumens.
How Many Watts Are Led Car Headlights/How Many Watts Does a Standard Headlight Have?
LED car headlights typically range between 20 to 50 watts per bulb, varying by the manufacturer and the model of the headlight.
Conclusion
Appreciating the wattage of your headlights is vital for both safety and compliance. Generally, standard headlights range between 40 to 60 watts. It’s important to check your vehicle’s manual or consult a professional to ensure you select the right wattage for optimal illumination.
Staying informed helps in maintaining clear visibility on the road.